While the first individual may be chosen by a random method subsequent members are chosen by means of a predetermined process. It requires the selection of a starting point for the sample and sample size that can be repeated at regular intervals.
Systematic Sampling Research Methodology
Linear systematic sampling is a systematic sampling method where samples arent repeated at.
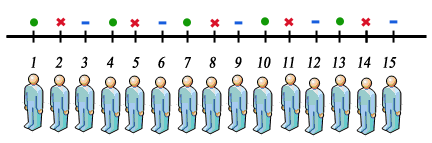
Explain systematic sampling. Systematic sampling is a technique for creating a random probability sample in which each piece of data is chosen at a fixed interval for inclusion in the sample. Systematic sampling has slightly variation from simple random sampling. In systematic random sampling the researcher first randomly picks the first item or subject from the population.
A systematic random sample relies on some sort of ordering to choose sample members. For example every fourth person in a list could be used in the sample. It has been stated that with systematic sampling every Kth item is selected to produce a sample of size n from a population size of N.
The most common form of systematic sampling is an equal-probability method. Systematic sampling and stratified sampling are the types of probability sampling design. Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which researchers select members of the population at a regular interval or k determined in advance.
Here only the first sampling unit is selected at random and the remaining units are automatically selected in a definite sequence at equal intervals. Systematic sampling is a random sampling technique which is frequently chosen by researchers for its simplicity and its periodic quality. Researchers use the systematic sampling method to choose the sample members of a population at regular intervals.
For example Lucas can. For example if a researcher wanted to create a systematic sample of 1000 students at a university with an enrolled population of 10000 he or she would choose every tenth person from a list of all students. In systematic sampling also called systematic random sampling every Nth member of population is selected to be included in the study.
Systematic sampling is a statistical method involving the selection of elements from an ordered sampling frame. Systematic sampling is more or less a method that involves the selection of various elements that are ordered from a sampling frame and taking this statistical procedure starts from the random selection of elements that belongs to a list and then every sampling interval from the frame is selected and this method of sampling can only be applied if at all the given population is homogeneous as these sample units are systematically. Systematic Sampling Method is another type of sampling method that is also called as interval samplingThis method uses an interval to choose the samples from a given population.
What are the types of systematic sampling. A simple random sample is a random sample chosen in such a way that each of the samples of that sample-size that can be chosen from the population has an equal probability of being selected as. Systematic random sampling is a method to select samples at a particular preset interval.
In this approach progression through the list is treated circularly with a return to the top once the end of the list is passed. Systematic sampling is a sampling technique that uses a predetermined system to select the participants from a target group. Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population.
Two things that you need to do or you need to have in systematic sampling is a list of names of all the members of the population then you need to assign numbers to each of the member of the population. It differs from random sampling in that it does not give an equal chance of selection to each individual in. Simple random sampling and systematic random sampling are both sampling techniques which result in random samples with a few different qualities.
Systematic sampling requires an approximated frame for a priori but not the full list. If the population order is random or random-like eg alphabetical then this method will give you a representative sample that can be used to draw conclusions about the population. It is a probability sampling method.
What is a Simple Random Sample.
ads
Citing Sources
Search This Blog
Labels
- 1000
- 1984
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- 2018
- ä¾å
- abbreviation
- abbreviations
- abide
- about
- abstract
- academic
- accept
- account
- accounting
- aces
- acknowledgement
- acknowledgements
- acknowledgment
- acronym
- action
- address
- adjective
- adjectives
- adviser
- affiliation
- after
- agreement
- agriculture
- aims
- alles
- alphabetical
- alphabetize
- alternative
- amazing
- amazon
- ambiguous
- american
- analyse
- analysis
- analyze
- annotated
- anonymous
- another
- answer
- apostrophe
- appendix
- application
- appointment
- approach
- approaches
- appropriate
- approximately
- architectural
- area
- argument
- argumentative
- around
- article
- articles
- aspirations
- assignment
- association
- assumption
- audience
- australia
- author
- authors
- auto
- automatic
- average
- avoid
- bachelor
- background
- ball
- bank
- banned
- based
- basics
- bear
- because
- before
- beginning
- being
- best
- between
- biased
- bible
- bibliographic
- bibliography
- bibme
- billion
- biography
- blind
- block
- blocking
- body
- book
- books
- break
- bullet
- business
- camera
- cannot
- capital
- capitalization
- capitalize
- capitalized
- cardinal
- career
- case
- catch
- catchy
- causal
- central
- change
- changes
- changing
- chapter
- characteristic
- charge
- chart
- check
- checker
- checkers
- checking
- chicago
- choose
- citation
- citations
- cite
- cited
- citer
- citing
- clarify
- class
- classification
- clauses
- coding
- collect
- collecting
- collection
- college
- collegiate
- colon
- colour
- comes
- comma
- commas
- common
- communication
- compare
- components
- compound
- concept
- conceptual
- concise
- conciseness
- conclusion
- conclusions
- confirm
- conjunction
- conjunctions
- construction
- contact
- containing
- content
- contents
- context
- continuous
- controlled
- convenience
- convert
- converter
- cool
- coordinating
- copied
- copy
- correct
- correction
- correlational
- correspondence
- corruption
- could
- countables
- cover
- create
- creating
- creator
- credible
- critical
- custodian
- data
- date
- dates
- deadline
- dedication
- deduction
- deductive
- default
- define
- defining
- definite
- definition
- degree
- dependent
- describe
- describing
- description
- descriptions
- descriptive
- design
- designs
- deutschland
- developer
- dialogue
- dictionary
- difference
- different
- direct
- disclosure
- discourse
- discuss
- discussion
- display
- dissertation
- distinguish
- docs
- doctor
- document
- documents
- docx
- does
- done
- down
- download
- draft
- easy
- easybib
- economic
- edit
- editing
- edition
- editor
- editors
- effective
- effectively
- elementary
- elements
- ellipses
- emotive
- empirical
- ending
- endnote
- endnotes
- engineering
- english
- equations
- equipment
- errors
- essay
- essays
- estilo
- evaluation
- evidence
- example
- examples
- experimental
- explain
- explained
- explanation
- expository
- express
- extended
- extension
- external
- face
- factor
- facts
- family
- fancy
- features
- figure
- figures
- file
- files
- findings
- first
- five
- fixer
- flexible
- focused
- follows
- font
- footnote
- footnotes
- form
- formal
- format
- formation
- formats
- formatting
- forms
- found
- four
- fraction
- framework
- france
- free
- freelance
- french
- from
- front
- full
- further
- future
- gather
- general
- generate
- generator
- geography
- german
- germany
- give
- glossary
- goals
- good
- government
- grade
- grammar
- grammarly
- great
- growth
- guide
- handbook
- happen
- harvard
- have
- having
- hdmi
- head
- header
- heading
- headings
- help
- helper
- history
- home
- hook
- however
- hundred
- hypothesis
- ideas
- identifying
- ieee
- illustration
- image
- images
- importance
- important
- improve
- included
- incorrect
- indefinite
- indent
- indentation
- independent
- index
- indirect
- induction
- inductive
- informal
- information
- initial
- inquisitive
- instead
- instructions
- inter
- interest
- interesting
- internal
- internet
- interview
- interviews
- into
- intranet
- introduce
- introducing
- introduction
- italicize
- italicized
- items
- itinerary
- jargon
- jobs
- join
- joint
- journal
- journals
- justification
- kindle
- kinds
- knowledge
- known
- label
- langer
- language
- large
- layout
- leadership
- lecture
- length
- letter
- letters
- level
- levels
- like
- limit
- limitations
- line
- lines
- linguistics
- link
- linking
- list
- lista
- literature
- logic
- login
- logistics
- long
- longer
- look
- looks
- lyrics
- machine
- magazine
- main
- make
- maker
- makes
- management
- manual
- manually
- manuscript
- many
- margins
- marketing
- marks
- mean
- meaning
- meanings
- meant
- measure
- measurement
- meeting
- mention
- merriam
- method
- methodology
- methods
- microsoft
- missing
- mistake
- model
- models
- modifier
- modifying
- more
- mosaic
- most
- movie
- movies
- much
- multiple
- music
- muss
- name
- names
- narrative
- naturalistic
- nature
- need
- netflix
- never
- newest
- news
- newspaper
- next
- night
- note
- noun
- nouns
- novel
- null
- number
- numbered
- numbers
- numerals
- objective
- objectives
- obvious
- office
- okay
- online
- openoffice
- order
- organise
- organization
- organized
- original
- other
- outline
- overall
- page
- pages
- paper
- papers
- paragraph
- paragraphs
- parallel
- paraphrase
- paraphrasing
- parenthesis
- parenthetical
- parenthetically
- part
- parts
- pass
- passive
- past
- paste
- patent
- patterns
- paypal
- people
- percentage
- perfect
- period
- person
- personal
- personality
- persuasive
- phrasal
- phrases
- physics
- pick
- picture
- pirate
- plagiarism
- plagiarized
- plan
- please
- plural
- poem
- poems
- poetry
- points
- polite
- political
- population
- possess
- possession
- possessive
- powerpoint
- poynter
- precis
- precise
- preliminary
- preposition
- prepositions
- present
- presentation
- press
- price
- primary
- printable
- private
- probability
- problem
- problems
- process
- professional
- professor
- program
- project
- projects
- pronoun
- pronouns
- proofread
- proofreading
- proper
- properly
- proposal
- psych
- psychological
- psychology
- publication
- published
- punctuation
- purdue
- purpose
- putting
- qualitative
- quality
- quantitative
- question
- questionnaire
- questions
- quick
- quiz
- quotation
- quote
- quotes
- quoting
- radio
- random
- rationale
- reading
- reasoning
- reasons
- redundancy
- reference
- references
- referencing
- refers
- region
- related
- relational
- relationship
- reliability
- remember
- remote
- report
- request
- require
- required
- research
- resources
- response
- results
- reuse
- review
- reviewing
- revision
- rhetorical
- right
- river
- rule
- rules
- runner
- safe
- sample
- sampling
- sayings
- scenes
- science
- scientific
- scope
- scratching
- search
- seasons
- second
- secondary
- section
- selection
- semicolon
- sentence
- sentences
- serbian
- series
- serve
- service
- services
- setup
- sheep
- sheet
- shona
- short
- shortcut
- shorten
- shortened
- should
- show
- sighted
- sign
- similar
- similarity
- simple
- singular
- site
- sites
- size
- slide
- small
- social
- software
- someone
- something
- songs
- source
- sources
- spaces
- spacing
- spanish
- speech
- spell
- spelling
- spss
- stable
- stage
- stages
- stanza
- start
- starters
- starting
- state
- statement
- statements
- stating
- statistics
- step
- steps
- story
- streaming
- structure
- structures
- student
- students
- study
- style
- styles
- subject
- subjective
- summarise
- summarize
- summarizing
- summary
- sure
- survey
- svenska
- synonym
- synopsis
- systematic
- table
- tables
- taboo
- take
- taken
- target
- teacher
- teachers
- techniques
- tekst
- tell
- template
- tense
- tenses
- tentative
- term
- terms
- test
- testing
- tests
- text
- textbook
- texting
- thanks
- that
- their
- thematic
- theme
- themes
- theoretical
- theory
- these
- thesis
- third
- those
- three
- through
- time
- times
- timetable
- title
- titles
- tone
- took
- tool
- tools
- topic
- topics
- track
- transcribe
- transcription
- transition
- transitional
- translated
- treatment
- trial
- turabian
- turn
- turnitin
- tweet
- types
- uber
- uncountable
- uncountables
- undergraduate
- union
- university
- unknown
- upload
- urkund
- usage
- used
- useful
- uses
- using
- vague
- valid
- validity
- vancouver
- variable
- variables
- various
- verb
- verbs
- versus
- very
- video
- visitor
- vocabulary
- voice
- voluntary
- water
- ways
- weak
- webpage
- website
- websites
- webster
- what
- whats
- when
- where
- whereas
- which
- widely
- wikipedia
- will
- with
- within
- without
- word
- words
- work
- works
- worth
- would
- write
- writing
- written
- york
- your
- yourself
- youtube
- youtuber
About Me
scratching on the 8 ball
Scratching On The 8 Ball Or 9 Ball Pool Rules LoveCueSports . Web Scratching on the 8 ball is considered a foul, as it is with 9 ball...

