Patanjali MishraAssistant ProfessorVMOU Kota. Administer the first half to all students then administer the second half to all students.
Cornerstones Of Assessment Online Presentation
Parallel-Forms Reliability and Clinical Utility of an Application Version of the Activity Card Sort Australia 18-64 The results suggest that further studies are required before the app version can be used for research or in clinical settings.
Parallel forms reliability. Parallel form reliability is also known as Alternative form reliability or Equivalent form reliability or Comparable form reliability. What is Parallel Forms Reliability. As noted correctly by Schriesheim et al alternate forms of.
Split a test in half. The process for calculating parallel forms reliability is as follows. Parallel form reliability estimation has an advantage over the test-retest method because we need not wait for a time period which is a debatable time period like say 15 days or 30 days.
You can utilize parallel forms of reliability when you have two different assessment tools for measuring similar things. Significance of Parallel form of reliability. Researchers can use different assessment tools in order to design questions for measuring similar things.
Parallel Forms reliability reliability is typically necessary when two separate versions of an instrument are used such as when the pre-test and post-test are different. Estimating reliability by means of the equivalent form method involves the use of two different but equivalent forms of the test. This system was referred to as test Under system-2 retrospective data for the last three months were collected by the supervisors which they called retest BBS 2004.
Thus the parallel form reliability is established Under the test-retest method data were collected under system-1 by the registrar on a regular basis. 4 Zeilen Parallel forms reliability means that if the same students take two different versions of a. As he indicated in his initial review the literature provides no examples of parallel form reliability as the term is usually used.
For example randomly split a 100-question test into Test A that contains 50 questions and. An EMPC- VMOU ProductionDr. It is a type of reliability that helps in measuring the correlation between two equivalent versions of a test.
Parallel forms reliability sometimes termed alternate forms reliability is one of the three primary classifications of psychometric reliability along with test-retest reliability and internal consistency reliability. So in that case we are having two parallel forms of a test. Reliability describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time.
Parallel forms reliability can help you test constructs. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Parallel forms Reliability It is a type of reliability that you can utilize for measuring the correlations between two similar versions of the test.
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia Redirected from Parallel-forms Reliability Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Researcher design number of versions for testing the reliability of research. Parallel forms reliability also called equivalent forms reliability uses one set of questions divided into two equivalent sets forms where both sets contain questions that measure the same construct knowledge or skill.
As a measurement model for the scores of parallel forms strict parallel measures are assumed so that the correlation between the scores ie the parallel-forms reliability or parallel-test reliability matches the reliability of both forms. In this method two parallel or equivalent forms of a test are used. Parallel forms of a test are different subsets of the same universe of items which capture the same attribute with the same accuracy.
The three categorizations of reliability differ primarily in the differing sources of non-trait or non-true score variability and. Inter-rater reliability is necessary if examinations are used and multiple researchers mark the examinations.
Reliability refers to the degree to which scores from a particular test are consistent from one use of the test to the next. In short here is a good reliability test definition.
Validity And Reliability Validity Is Concerned With Getting The Right Assessment And Reliabilit Social Science Research Problem Solving Activities Assessment
Validity refers to how well a test measures what it is purported to measure.
Validity and reliability in assessment. Reliability and validity are key concepts in the field of psychometrics which is the study of theories and techniques involved in psychological measurement or assessment. Validity refers to the degree to which a test score can be interpreted and used for its intended purpose. Why is it necessary.
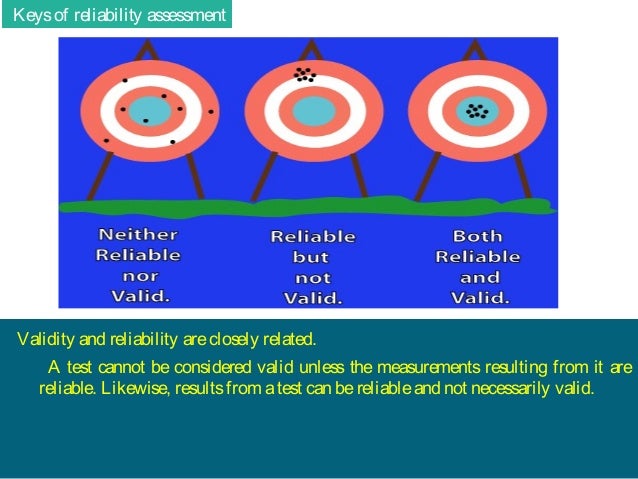
Likewise results from a test can be reliable and not necessarily valid. One can easily assess the reliability of the measuring instrument however to assess validity is difficult. Assessment validity is a bit more complex because it is more difficult to assess than reliability.
Reliability and validity influence tests and assessments in various ways. Validity and reliability are meaningful measurements that should be taken into account when attempting to evaluate the status of or progress toward any objective a. Any assessment is a balance between validity and reliability.
The science of psychometrics forms the basis of psychological testing and assessment which involves obtaining an objective and standardized measure of the behavior and. Reliability asks whether the actual metric is constructed sufficiently to produce results that are consistent. However new perspective proposes that assessment should be included.
It is very important to ensure that these two concepts are achieved in every test Buelow Hinkle 2008. The traditional practice is for evaluating outcomes is an Assessment of Learning. Validity focuses on accuracy ie.
Conversely reliability concentrates on precision which measures the extent to which scale produces consistent outcomes. As earlier mentioned reliability has a huge effect on the degree of consistency achieved by test results in terms of their accuracy and dependability. Just as we enjoy having reliable cars cars that start every time we need them we strive to have reliable consistent instruments to measure student achievement.
Validity and reliability of assessment methods are considered the two most important characteristics of a well-designed assessment procedure. A test cannot be considered valid unless the measurements resulting from it are reliable. It checks whether the scale produces expected results or not.
Keys of reliability assessment Validity and reliability are closely related. The different types of validity include. If the results are inconsistent the test is not considered reliable.
Reliability refers to the extent to which assessments are consistent. For example if your scale is off by 5 lbs it reads your weight every day with an excess of 5lbs. Reliability is a very important piece of validity evidence.
While validity pulls in the direction of open and authentic assessment of the whole subject reliability pulls in the opposite direction with closed tasks which would have high interrater reliability. Presentation Validity Reliability 1. While reliability is necessary it alone is not sufficient.
Validity refers to the degree to which a method assesses what it claims or intends to assess. Validity asks whether the interpretation of the results obtained from the metric used actually inform what is intended to be measured. Reliability and validity are two concepts that are important for defining and measuring bias and distortion.
For a test to be reliable it also needs to be valid. VALIDITY RELIABILITY PRACTICALITY Prof. If an assessment is reliable your results will be very similar no matter when you take the test.
The need for accuracy of data should influence the choice of equipment for conducting first-hand investigations. Freedom from mistakes this exemption arising from carefulness.
What S The Difference Between Reliability Accuracy And Validity How Can They Be Improved Youtube
If a piece of information is reliable then it is also credible.
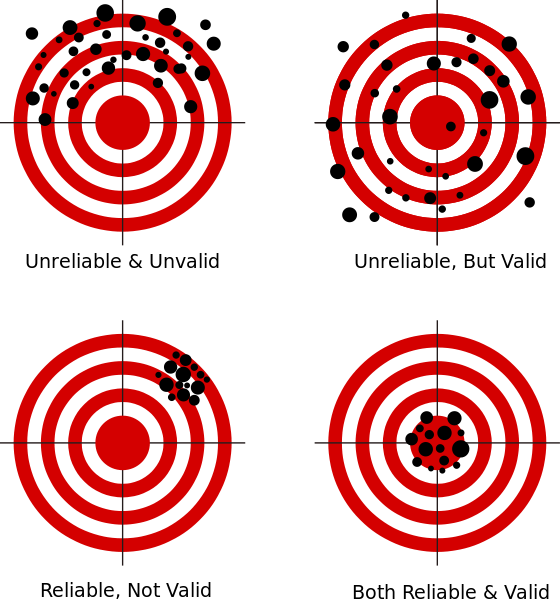

What is the difference between reliability and accuracy. Matt Anticole explains what exactly precision is and how can help us to measure things better. Reliability can be used to understand how well the service will be available in context of different real-world conditions. It could be the same wrong result each time An experiment where you can actually demonstrate by other means that its representative of a true value is accurate.
This article will break down the fundamental differences between. Looking at the process of measurement more carefully you will see that there is another important consideration. When we measure things most people are only worried about how accurate or how close to the actual value they are.
The degree of resemblance among study results were the study to be repeated under similar circumstances. Consistency and accuracy are trigger words for examiners use them correctly and your marker will be confident that youve understood. Free from failure error or defect.
If you can do the experiment over and over ie repetitions and get the same result then your results are reliable. Reliability is about a methods consistency and validity is about its accuracy. These are certain preferred qualities which gauge the goodness in measuring the characteristics under consideration.
For the purpose of checking the accuracy and applicability a multi-item measurement scale needs to be evaluated in terms of reliability validity and generalizability. Accuracy symbolizes the extent of conformity whereas Precision indicates the extent of reproducibility. In public health the terms accuracy precision validity and reliability mean the following.
How close a measurement is to the true value. The degree to which a measurement represents the true value of something. What is reliability.
Cross-validation sometimes called rotation estimation or out-of-sample testing is any of various similar model validation techniques for assessing how the results of a statistical analysis will generalize to an independent data set. You can assess both using various types of evidence. For instance a cloud solution may be available with an SLA commitment of 99999 percent but.
Where data is collected quantified or evaluated reliability refers to the ability of the data gathering process to provide results that are consistent and within expected ranges. It is important that we encourage students to predict expected results and even predict ranges of data. There are two common definitions of accuracy.
As an accurate calculator. Correctness while reliability is the quality of being reliable dependable or trustworthy. The ISO International Organization for Standardization applies a more rigid definition where accuracy refers to a measurement with both true and consistent results.
In math science and engineering accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the true value. When we discuss consistency we are looking at how well the test functions. Reliability is how correct the experiment is.
Uncertainty is the range of values where the true value or actual location of the measurement results UUC lie while the Error is the exact result of the difference between the UUC and STD which shows how accurate the measurement result is by showing the actual distance to the true STD value. Credibility refers to whether something can be believed as true. What is the difference between Reliability and Credibility.
In short Reliability refers to consistency and Validity refers to accuracy. As nouns the difference between accuracy and reliability is that accuracy is the state of being accurate. Reliability refers to the probability that the system will meet certain performance standards in yielding correct output for a desired time duration.
Reliability refers to relying on someone or something or being able to have trust and faith. Validity is all about the genuineness of the research whereas reliability is nothing but the repeatability of the outcomes. Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions.
The result of care or pains. Accurate expression knowledge etc while reliable is. You can improve accuracy by using better apparatus eg digital equipment etc.
Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure. As adjectives the difference between accurate and reliable is that accurate is in exact or careful conformity to truth. An experiment where you can repeat it many times and get all results close to one another is very reliable.
Directed by Anton Bogaty narrated by Addison Anderson. Accuracy is how precise the experiment is. It is mainly used in settings where the goal is prediction and one wants to estimate how accurately a predictive model will perform in practice.
At the time of taking measurements these two are always taken into account due to their utmost importance in the various field such as science statistics research and engineering.
1995 found that inter-rater agreement for continuous scores on either the total SIDP-R score or scores from Clusters A B and C was satisfactory 1CCs ranging from 082 to 090. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click on.
Inter Rater Reliability Wikipedia
Using the SIDP-R Pilkonis et al.

Low inter rater reliability. You want to calculate inter-rater reliability. Inter-rater Reliability of the McKenzie Method of Mechanical Diagnosis and Therapy for the Provisional Classification of Low Back Pain in Adolescents and Young Adults J Man Manip Ther. Inter-rater reliability was quantified as the intraclass correlation coefficient ICC using the two-way random effects model with consistency.
These findings extend beyond those of prior research. Several investigations of inter-rater reliability reveal poor to good agreement. Inter-rater reliability IRR is the process by which we determine how reliable a Core Measures or Registry abstractors data entry is.
Inter-Rater Reliability refers to statistical measurements that determine how similar the data collected by different raters are. Inter-rater reliability for presence or absence of any personality disorder with the SIDP-R was moderate with a kappa of. Oddveig Birkeflet Petter Laake and Nina Vøllestad.
1 the letter of reference LOR 2 the multi-item 3 the. Noelle Wyman Roth of Duke University answers common questions about working with different software packages to help you in your qualitative data research an. The method for calculating inter-rater reliability will depend on the type of data categorical ordinal or continuous and the number of coders.
A score of 1 means perfect inter-rater agreement. Low inter-rater reliability values refer to a low degree of agreement between two examiners. In psychosocial research a kappa score of 07 or above is generally considered good.
Suppose this is your data set. The Kappa statistic is a measure of inter-rater reliability. A score of 0 indicates zero agreement.
The authors found high inter-rater reliability ICC 093 but only moderate intra-rater reliability ICC 060 for pain pressure. As such the goal of this study is to develop alternate job reference formats and compare their inter-rater reliability. It consists of 30 cases rated by three coders.
It includes different forms of the same test performed on the same participants. 4 job reference formats will be compared. If you have the appropriate software installed you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice.
Inter-rater reliability was rather poor and there were no significant differences between evaluations from reviewers of the same scientific discipline as the papers they were reviewing versus reviewer evaluations of papers from disciplines other than their own. Inter-rater reliability is measured by a statistic called a kappa score. Acupuncture in Medicine 2011 29.
Of the research available the inter-rater reliability of letters of reference LORs tends to be low as a result of various biases including leniency lack of information or memory retrieval. Examples of raters would be a job interviewer a psychologist measuring how many times a subject scratches their head in an experiment and a scientist observing how many times an. It shows that the questionnaire has low inter-rater reliability.
Suppose five researchers measure the academic performance of the same student by incorporating various questions from all the academic subjects and submit various results. There is no absolute value for good agreement and depends on the nature of the study. Low Inter-Rater Reliability in Traditional Chinese Medicine for Female Infertility.
The intra-rater SEM ranged between 79 and 100 kPa. It is a score of how much consensus exists in ratings and the level of agreement among raters observers coders or examiners. 1 51-57 Download Citation.
However Van Wilgen Van der Noord Zwerver 2011 found lower values for intra-rater reliability compared to inter-rater reliability of pressure algometry in healthy volleyball athletes and those with patellar tendinopathy. Be aware that in some circumstances it is possible to have great agreement but a low Kappa. Examples of the use of inter-rater reliability in neuropsychology include a the evaluation of the consistency of clinicians neuropsychological diagnoses b the evaluation of scoring parameters on drawing tasks such as the Rey Complex Figure Test or Visual Reproduction subtest and c the.
A rater is someone who is scoring or measuring a performance behavior or skill in a human or animal. Cohen was a busy guy he did lots of stuff. Unfortunately the inter-rater reliability of the eight doctors was low ICC 350 single measures.
Use an appropriate questionnaire to measure the competency level. Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure of a concept.
Testing And Assessment Reliability And Validity
There are three factors researchers generally use to assess whether a measure is reliable.

Reliability in research. Oftentimes researchers repeat research in different settings to compare the reliability of the research. It is a test. In this method the researcher performs a similar test over some time.
Threats to reliability Types of methodsmeasures of reliability How do I use these tests of reliability. If we administer a measure to a group and then re-administer it and there is little. Reliability in research entails the concerns the stability consistency of the data as well as homogeneous repeatability of the results if several tests are done LoBiondo-Wood Haber 2014.
Analyze the research items regularly to avoid poor. Well begin by defining a measure that well arbitrarily. Ensure a consistent environment for participants Make the participants familiar with the criteria of assessment.
Like reliability and validity as used in quantitative. Reliability in research What is reliability. Various researchers address these issues of validity and reliability in different.
How to Increase Reliability. Reliability in research can be referred to as a way of analyzing the quality of the measurement. 7 September 15 2019.
Types of Reliability in Research Reliability. Understanding Reliability and Validity in Qualitative Research Abstract The use of reliability and validity are common in quantitative research and now it is reconsidered in the qualitative research paradigm. Lets explore in more detail what it means to say that a measure is repeatable or consistent.
On the other hand validity entails the accuracy and integrity of the data or results collected from the various tests that a researcher performs. Different types of Reliability. In the research reliability is the degree to which the results of the research are consistent and repeatable.
When you apply the same method to the same sample under the same conditions you should get the same results. Test-retest reliability relates to the measure of reliability that has been obtained by conducting the same test more. In research the term reliability means repeatability or consistency.
Stability aka test-retest reliability is the measure stable over time or do the results fluctuate. Finally a reliable and reproducible research outcome yield new theories. Reliability and validity are concepts used to evaluate the quality of research.
When you do quantitative research you have to consider the reliability and validity of your research methods and instruments of measurement. Reliability tells you how consistently a method measures something. Train the participants appropriately.
Reliability is the degree to which a test gives the same results each time that it is used assuming that the thing being measured does not change. The function of reliability in research is to ensure that the observed score is almost similar to true score obtained by minimizing the errors in measurement. They indicate how well a method technique or test measures something.
Parallel forms reliability relates to a measure that is obtained by conducting assessment of the same phenomena. Research reliability can be divided into three categories. Reliability is about the consistency of a measure and validity is about the accuracy of a measure.
A measure is considered reliable if it would give us the same result over and over again assuming that what we are measuring isnt changing. Since reliability and validity are rooted in positivist perspective then they should be redefined for their use in a naturalistic approach.
ads
Citing Sources
Search This Blog
Labels
- 1000
- 1984
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- 2018
- ä¾å
- abbreviation
- abbreviations
- abide
- about
- abstract
- academic
- accept
- account
- accounting
- aces
- acknowledgement
- acknowledgements
- acknowledgment
- acronym
- action
- address
- adjective
- adjectives
- adviser
- affiliation
- after
- agreement
- agriculture
- aims
- alles
- alphabetical
- alphabetize
- alternative
- amazing
- amazon
- ambiguous
- american
- analyse
- analysis
- analyze
- annotated
- anonymous
- another
- answer
- apostrophe
- appendix
- application
- appointment
- approach
- approaches
- appropriate
- approximately
- architectural
- area
- argument
- argumentative
- around
- article
- articles
- aspirations
- assignment
- association
- assumption
- audience
- australia
- author
- authors
- auto
- automatic
- average
- avoid
- bachelor
- background
- ball
- bank
- banned
- based
- basics
- bear
- because
- before
- beginning
- being
- best
- between
- biased
- bible
- bibliographic
- bibliography
- bibme
- billion
- biography
- blind
- block
- blocking
- body
- book
- books
- break
- bullet
- business
- camera
- cannot
- capital
- capitalization
- capitalize
- capitalized
- cardinal
- career
- case
- catch
- catchy
- causal
- central
- change
- changes
- changing
- chapter
- characteristic
- charge
- chart
- check
- checker
- checkers
- checking
- chicago
- choose
- citation
- citations
- cite
- cited
- citer
- citing
- clarify
- class
- classification
- clauses
- coding
- collect
- collecting
- collection
- college
- collegiate
- colon
- colour
- comes
- comma
- commas
- common
- communication
- compare
- components
- compound
- concept
- conceptual
- concise
- conciseness
- conclusion
- conclusions
- confirm
- conjunction
- conjunctions
- construction
- contact
- containing
- content
- contents
- context
- continuous
- controlled
- convenience
- convert
- converter
- cool
- coordinating
- copied
- copy
- correct
- correction
- correlational
- correspondence
- corruption
- could
- countables
- cover
- create
- creating
- creator
- credible
- critical
- custodian
- data
- date
- dates
- deadline
- dedication
- deduction
- deductive
- default
- define
- defining
- definite
- definition
- degree
- dependent
- describe
- describing
- description
- descriptions
- descriptive
- design
- designs
- deutschland
- developer
- dialogue
- dictionary
- difference
- different
- direct
- disclosure
- discourse
- discuss
- discussion
- display
- dissertation
- distinguish
- docs
- doctor
- document
- documents
- docx
- does
- done
- down
- download
- draft
- easy
- easybib
- economic
- edit
- editing
- edition
- editor
- editors
- effective
- effectively
- elementary
- elements
- ellipses
- emotive
- empirical
- ending
- endnote
- endnotes
- engineering
- english
- equations
- equipment
- errors
- essay
- essays
- estilo
- evaluation
- evidence
- example
- examples
- experimental
- explain
- explained
- explanation
- expository
- express
- extended
- extension
- external
- face
- factor
- facts
- family
- fancy
- features
- figure
- figures
- file
- files
- findings
- first
- five
- fixer
- flexible
- focused
- follows
- font
- footnote
- footnotes
- form
- formal
- format
- formation
- formats
- formatting
- forms
- found
- four
- fraction
- framework
- france
- free
- freelance
- french
- from
- front
- full
- further
- future
- gather
- general
- generate
- generator
- geography
- german
- germany
- give
- glossary
- goals
- good
- government
- grade
- grammar
- grammarly
- great
- growth
- guide
- handbook
- happen
- harvard
- have
- having
- hdmi
- head
- header
- heading
- headings
- help
- helper
- history
- home
- hook
- however
- hundred
- hypothesis
- ideas
- identifying
- ieee
- illustration
- image
- images
- importance
- important
- improve
- included
- incorrect
- indefinite
- indent
- indentation
- independent
- index
- indirect
- induction
- inductive
- informal
- information
- initial
- inquisitive
- instead
- instructions
- inter
- interest
- interesting
- internal
- internet
- interview
- interviews
- into
- intranet
- introduce
- introducing
- introduction
- italicize
- italicized
- items
- itinerary
- jargon
- jobs
- join
- joint
- journal
- journals
- justification
- kindle
- kinds
- knowledge
- known
- label
- langer
- language
- large
- layout
- leadership
- lecture
- length
- letter
- letters
- level
- levels
- like
- limit
- limitations
- line
- lines
- linguistics
- link
- linking
- list
- lista
- literature
- logic
- login
- logistics
- long
- longer
- look
- looks
- lyrics
- machine
- magazine
- main
- make
- maker
- makes
- management
- manual
- manually
- manuscript
- many
- margins
- marketing
- marks
- mean
- meaning
- meanings
- meant
- measure
- measurement
- meeting
- mention
- merriam
- method
- methodology
- methods
- microsoft
- missing
- mistake
- model
- models
- modifier
- modifying
- more
- mosaic
- most
- movie
- movies
- much
- multiple
- music
- muss
- name
- names
- narrative
- naturalistic
- nature
- need
- netflix
- never
- newest
- news
- newspaper
- next
- night
- note
- noun
- nouns
- novel
- null
- number
- numbered
- numbers
- numerals
- objective
- objectives
- obvious
- office
- okay
- online
- openoffice
- order
- organise
- organization
- organized
- original
- other
- outline
- overall
- page
- pages
- paper
- papers
- paragraph
- paragraphs
- parallel
- paraphrase
- paraphrasing
- parenthesis
- parenthetical
- parenthetically
- part
- parts
- pass
- passive
- past
- paste
- patent
- patterns
- paypal
- people
- percentage
- perfect
- period
- person
- personal
- personality
- persuasive
- phrasal
- phrases
- physics
- pick
- picture
- pirate
- plagiarism
- plagiarized
- plan
- please
- plural
- poem
- poems
- poetry
- points
- polite
- political
- population
- possess
- possession
- possessive
- powerpoint
- poynter
- precis
- precise
- preliminary
- preposition
- prepositions
- present
- presentation
- press
- price
- primary
- printable
- private
- probability
- problem
- problems
- process
- professional
- professor
- program
- project
- projects
- pronoun
- pronouns
- proofread
- proofreading
- proper
- properly
- proposal
- psych
- psychological
- psychology
- publication
- published
- punctuation
- purdue
- purpose
- putting
- qualitative
- quality
- quantitative
- question
- questionnaire
- questions
- quick
- quiz
- quotation
- quote
- quotes
- quoting
- radio
- random
- rationale
- reading
- reasoning
- reasons
- redundancy
- reference
- references
- referencing
- refers
- region
- related
- relational
- relationship
- reliability
- remember
- remote
- report
- request
- require
- required
- research
- resources
- response
- results
- reuse
- review
- reviewing
- revision
- rhetorical
- right
- river
- rule
- rules
- runner
- safe
- sample
- sampling
- sayings
- scenes
- science
- scientific
- scope
- scratching
- search
- seasons
- second
- secondary
- section
- selection
- semicolon
- sentence
- sentences
- serbian
- series
- serve
- service
- services
- setup
- sheep
- sheet
- shona
- short
- shortcut
- shorten
- shortened
- should
- show
- sighted
- sign
- similar
- similarity
- simple
- singular
- site
- sites
- size
- slide
- small
- social
- software
- someone
- something
- songs
- source
- sources
- spaces
- spacing
- spanish
- speech
- spell
- spelling
- spss
- stable
- stage
- stages
- stanza
- start
- starters
- starting
- state
- statement
- statements
- stating
- statistics
- step
- steps
- story
- streaming
- structure
- structures
- student
- students
- study
- style
- styles
- subject
- subjective
- summarise
- summarize
- summarizing
- summary
- sure
- survey
- svenska
- synonym
- synopsis
- systematic
- table
- tables
- taboo
- take
- taken
- target
- teacher
- teachers
- techniques
- tekst
- tell
- template
- tense
- tenses
- tentative
- term
- terms
- test
- testing
- tests
- text
- textbook
- texting
- thanks
- that
- their
- thematic
- theme
- themes
- theoretical
- theory
- these
- thesis
- third
- those
- three
- through
- time
- times
- timetable
- title
- titles
- tone
- took
- tool
- tools
- topic
- topics
- track
- transcribe
- transcription
- transition
- transitional
- translated
- treatment
- trial
- turabian
- turn
- turnitin
- tweet
- types
- uber
- uncountable
- uncountables
- undergraduate
- union
- university
- unknown
- upload
- urkund
- usage
- used
- useful
- uses
- using
- vague
- valid
- validity
- vancouver
- variable
- variables
- various
- verb
- verbs
- versus
- very
- video
- visitor
- vocabulary
- voice
- voluntary
- water
- ways
- weak
- webpage
- website
- websites
- webster
- what
- whats
- when
- where
- whereas
- which
- widely
- wikipedia
- will
- with
- within
- without
- word
- words
- work
- works
- worth
- would
- write
- writing
- written
- york
- your
- yourself
- youtube
- youtuber
About Me
scratching on the 8 ball
Scratching On The 8 Ball Or 9 Ball Pool Rules LoveCueSports . Web Scratching on the 8 ball is considered a foul, as it is with 9 ball...

