Then choose a simple random sample from each stratum. Systematic sample - A systematic sample is chosen on the basis of an ordered system.
Multi-stage sampling is a combination of at least two methods of sampling.

What are the types of sampling. Sampling is a method used in statistical analysis in which a decided number of considerations are taken from a comprehensive population or a sample survey. To create a representative sample researchers take a simple random sample from each stratum. Combine those into the overall sample.
To Avoid Working Late A Quality Control Analyst Simply Inspects The First 100 Items Produced In A Day. Probability sampling Non-probability sampling. Probability samples or non-probability samples.
Types of Sampling We may then consider different types of probability samples. The selection of cases with maximum variation for the purpose of documenting unique or diverse variations that have emerged in adapting to different. Simple Random Stratified Systematic Or Convenience.
Cluster sample A cluster sample involves using a simple random sample of evident groups that the population contains. If the population is everyone who has bought a lottery ticket then each person has an equal chance of winning the lottery assuming they all have one ticket each. Although there are a number of different methods that might be used to create a sample they generally can be grouped into one of two categories.
Probability sampling where subjects are selected randomly or on a probability basis and the second is non-probability sampling where subjects. Divide the population into strata. Types of studies experimental vs.
Identify Which Of These Types Of Sampling Is Used. Techniques for random sampling and avoiding bias. O Convenience O Stratified O Systematic Simple Random.
Examples include the selection of extreme or deviant outlier cases for the purpose of learning from an unusual manifestations of phenomena of interest. There can be any number of these. Random sampling is a type of probability sampling where everyone in the entire target population has an equal chance of being selected.
This is the currently selected item. As suggested probability sampling is a type of sampling in which every single member of a group has an equal probability of being selected for the survey. Stratified sample - A stratified sample results when a population is split into at least two non-overlapping sub-populations.
This method can be used if the population has a. There are two types of sampling. There are two basic types of sampling methods.
Types of purposeful sampling designs There exist numerous purposeful sampling designs. Then a random sampling is done on those groups to get a sample. This is similar to the national lottery.
One study may incorporate several groups. Probability sampling can still exist within a filtered group such as American adults as long as every representative of this subgroup has an equal chance of. First the population is divided into non-overlapping subpopulations or groups.
Stratified sampling is a variation of random sampling that involves dividing the population into distinct groups or strata This method aims to make samples more representative of the population. The methodology used to sample from an extensive population depends on the type of study being conducted but may involve simple random sampling or systematic sampling. 9 rows Sampling in market research is of two types probability sampling and non-probability.
Heshe numbers each element of the population from 1-5000 and will choose every 10th individual to be a part of the sample Total population Sample Size 5000500 10. A periodic sampling method selects every nth item from the data set.
Real world examples of simple random sampling include.
Data sampling examples. For example if you choose every 3 rd item in the dataset thats periodic sampling Note. Example You use simple random sampling to choose subjects from within each of your six groups selecting a roughly equal sample size from each one. For example if N 7 and n 2 k35.
For example a researcher intends to collect a systematic sample of 500 people in a population of 5000. Several variants of adaptive sampling have been proposed in the literature. If we consider k3 the samples will be ad be ca db and ec.
A sample is created by setting an interval at which to extract data from the larger population -- for example selecting every 10th row in a spreadsheet of 200 items to create a sample size of 20 rows to analyze. So you go to the park and. A convenient sample is when members or objects are chosen based on convenience and availability.
In circular systematic sampling a sample starts again from the same point once again after ending. For instance in locally adaptive sampling intervals between samples is computed using a function of previously taken. For example the first element will be chosen at random then every tenth element will be included in the sample.
Two students carry three books one student carries four books one student carries two books and one student carries one book. For example you have to select the top 3 students from each class. In case of systematic sampling the first element in the sample is chosen at random.
In this You have a given condition and you have to pick up sample according to that condition. For example suppose you are interested in studying peoples opinions about a new park in the community. Frequently asked questions about stratified sampling.
You sample five students. Elements are selected until exact proportions of certain types of data is obtained or sufficient data in different categories is collected. You can then collect data on salaries and job histories from each of the members of your sample to investigate your question.
In this sampling you pick up the members from the population through a well-defined system to make a Sample. On an assembly line each employee is assigned a random number using computer software. Data Science is the study of algorithms.
In probability sampling every member of population has a known chance of participating in the study. Probability Sampling may be a sampling technique during which sample from a bigger population are chosen employing a method supported the idea of probabilityFor a participant to be considered as a probability sample heshe must be selected employing a random selection. Probability sampling methods include simple stratified systematic multistage and cluster sampling methods.
Data Sample of Quantitative Discrete Data The data are the number of books students carry in their backpacks. From the name you can think what is the Systematic Sampling. If our population has 45 females and 55 males then our sample should reflect the same percentage of males and females.
Then the next elements are chosen in a systematic fashion. There are two probable ways to form sample. This post is about some of the most common sampling techniques one can use while working with data.
I grapple through with many algorithms on a day to day basis so I thought of listing some of the most common and most used algorithms one will end up using in this new DS Algorithm series. The numbers of books three four two and one are the quantitative discrete data. At a birthday party teams for a game are chosen by putting everyones name into a jar and then choosing the names at random for each team.
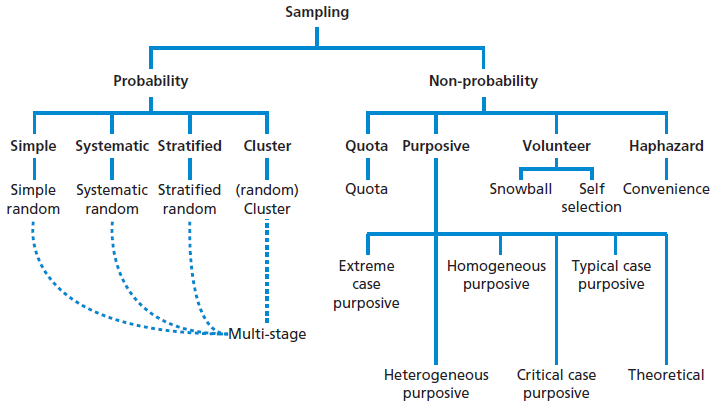
Types of Sampling in Primary Data Collection Sampling methods are broadly divided into two categories.
This is similar to the national lottery. There are a number of techniques of taking Probability sample.
Sampling Methods Types And Techniques Explained
Random sampling an.
5 types of sampling techniques. An example of this could be school or college. Now let us discuss three different types of sampling techniques in detail. There are two basic types of sampling methods.
TYPES OF SAMPLING 1. Before choosing a method the researcher must find a sampling frame this is the collection of people the researcher will then choose their sample from. All the members have an equal opportunity to be a part of the.
What is probability sampling. Units Types 516. The purest form of sampling under the probability approach random sampling provides equal chances of being picked for each member of the target population.
Types of Sampling Methods. Simple Random Sampling SRS Stratified Sampling Cluster Sampling Systematic Sampling. I Instantaneous sampling ii Natural sampling iii Flat top sampling Out of these three instantaneous sampling is called ideal sampling whereas natural sampling and flat-top sampling are called practical sampling methods.
Lets take a closer look at these two methods of sampling. The one chosen will depend on a number of factors such as time money etc. There are four types of Non-probability sampling techniques.
There are numerous ways of getting a sample but here are the most commonly used sampling methods. Supplies Glassware More 844 Understanding Laboratory Measurements. Every piece of research requires a sample and there are many ways of finding a suitable sample.
Sampling Techniques Basically there are three types of sampling techniques such as. The following sampling methods are examples of probability sampling methods. There are various sampling methods.
Probability sampling is a sampling technique where a researcher sets a selection of a few criteria and chooses members of a population randomly. Multiple or Double sampling. This is the currently selected item.
Non-probability sampling involves non-random selection based on convenience or other criteria allowing you to easily collect initial data. Types or Techniques Probability Sampling. There are four types of probability sampling techniques.
There are two types of sampling methods- 1 Random Sampling Method 2 Non-Random Sampling Method. But here only six important techniques have been discussed as follows. Sampling in market research is of two types probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
Includes Quota sampling Snowball sampling Judgment sampling a nd Convenience sampling furthermore Probability Sampling includes Simple random Stratified random Cluster sampling Systematic. In simple words probability sampling also known as random sampling or chance sampling utilizes random sampling techniques and principles to create a sample. Revise abiotic and biotic factors and sampling techniques such as using quadrats and pitfall traps as part of National 5 Biology.
Types of studies experimental vs. Sampling Techniques In Scientific Investigations 740 Chemistry Lab Equipment. Random sampling is a type of probability sampling where everyone in the entire target population has an equal chance of being selected.
Techniques for random sampling and avoiding bias.
If you approach the higher authorities in an organization so that you can conduct a survey on its employees you may not receive permission for doing so. A convenience sample chooses the individuals that are easiest to reach or sampling that is done easy.
Convenience Sampling In Research Methodology
Convenience samples are an excellent way to intervene.

What is convenience sampling. Convenience Sampling with Examples Convenience sampling is a sampling technique in which you collect samples of data from people who are easily accessible to you. In other words the sample is selected based on availability and not according to more elaborate screening processes. Convenience sampling is an affordable way to gather data.
Convenience sampling does not represent the entire population so it is considered bias. Convenience Sampling also known as availability sampling is a non-probability non-random sampling method used to generate samples according to the ease of access readiness to be part of the sample accessibility at a specified time slot or any other practical requirements of a specific component. It is useful as an intervention to correct dissatisfaction.
For example standing at a mall or a grocery store and asking people to answer questions would be an example of a convenience. Convenience sampling is a type of nonprobability sampling in which people are sampled simply because they are convenient sources of data for researchers. Convenience Sampling is a special kind of Non-Probability sampling where sample will be choose randomly from population and there have also unrestricted term.
It doesnt take much effort to start a convenience. This is different from random sampling. This is convenience sampling improperly used.
Convenience Samples A convenience sample consists of research subjects who were chosen for a study because they could be recruited easily. It is a type of nonprobability sampling that focuses on a sample that is easy to access and readily available. As the name describes the researcher chooses subjects because of convenience.
Convenience sampling is a type of nonprobability sampling technique in which subjects are selected on their convenient access ability as well as proximity to the researcher. Sometimes a convenience sample is called a grab sample as we essentially grab members from the population for our sample. However they may.
Inexpensive to create samples. In situations where time is a constraint many researchers choose this method for quick data. A convenience sample is formed when we select elements from a population on the basis of what elements are easy to obtain.
One advantage of convenience. Convenience Sampling is a statistical technique to gather data from subjects that are conveniently accessible. In convenience sampling the selection of units from the population is.
Here are the advantages of adopting a convenience sampling approach. This method is also called the chunk fraction taken from the population on the basis of its convenient accessibility and availability to the investigator. The money and time invested in.
The Convenience Sampling is the non-probability sampling technique wherein a proportion of the population is selected on the basis of its convenient availability. With this method the researcher uses subjects that are easy to reach. A Convenience sampling constitutes probability sampling b Convenience sampling promotes external validity c Convenience sampling threatens internal validity in a clinical trial.
In probability sampling each element in the population has a known nonzero chance of being selected through the use of a. List of the Advantages of Convenience Sampling 1. Convenience sampling is a sampling method where the researcher selects the research sample based on ease and proximity to the researcher.
We have all seen studies that leverage students in the computer science classes. It is also known as availability sampling. Convenience sampling sometimes called accidental sampling is the selection of a sample of participants from a population based on how convenient and readily available that group of participants is.
Convenience sampling is a method of collecting samples by taking samples that are conveniently located around a location or Internet service. One disadvantage of convenience sampling is that subjects in a convenience sample may not be representative of the. Facebook questions can be one of the popular methods of convenience sampling.
Convenience sampling was used to recruit participants from patients admitted to one of six hospitals in the west of Scotland with an acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Convenience sampling is also known as grab opportunity accidental or haphazard sampling.
While the first individual may be chosen by a random method subsequent members are chosen by means of a predetermined process. It requires the selection of a starting point for the sample and sample size that can be repeated at regular intervals.
Systematic Sampling Research Methodology
Linear systematic sampling is a systematic sampling method where samples arent repeated at.
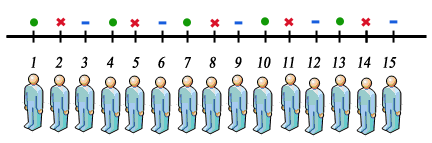
Explain systematic sampling. Systematic sampling is a technique for creating a random probability sample in which each piece of data is chosen at a fixed interval for inclusion in the sample. Systematic sampling has slightly variation from simple random sampling. In systematic random sampling the researcher first randomly picks the first item or subject from the population.
A systematic random sample relies on some sort of ordering to choose sample members. For example every fourth person in a list could be used in the sample. It has been stated that with systematic sampling every Kth item is selected to produce a sample of size n from a population size of N.
The most common form of systematic sampling is an equal-probability method. Systematic sampling and stratified sampling are the types of probability sampling design. Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which researchers select members of the population at a regular interval or k determined in advance.
Here only the first sampling unit is selected at random and the remaining units are automatically selected in a definite sequence at equal intervals. Systematic sampling is a random sampling technique which is frequently chosen by researchers for its simplicity and its periodic quality. Researchers use the systematic sampling method to choose the sample members of a population at regular intervals.
For example Lucas can. For example if a researcher wanted to create a systematic sample of 1000 students at a university with an enrolled population of 10000 he or she would choose every tenth person from a list of all students. In systematic sampling also called systematic random sampling every Nth member of population is selected to be included in the study.
Systematic sampling is a statistical method involving the selection of elements from an ordered sampling frame. Systematic sampling is more or less a method that involves the selection of various elements that are ordered from a sampling frame and taking this statistical procedure starts from the random selection of elements that belongs to a list and then every sampling interval from the frame is selected and this method of sampling can only be applied if at all the given population is homogeneous as these sample units are systematically. Systematic Sampling Method is another type of sampling method that is also called as interval samplingThis method uses an interval to choose the samples from a given population.
What are the types of systematic sampling. A simple random sample is a random sample chosen in such a way that each of the samples of that sample-size that can be chosen from the population has an equal probability of being selected as. Systematic random sampling is a method to select samples at a particular preset interval.
In this approach progression through the list is treated circularly with a return to the top once the end of the list is passed. Systematic sampling is a sampling technique that uses a predetermined system to select the participants from a target group. Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population.
Two things that you need to do or you need to have in systematic sampling is a list of names of all the members of the population then you need to assign numbers to each of the member of the population. It differs from random sampling in that it does not give an equal chance of selection to each individual in. Simple random sampling and systematic random sampling are both sampling techniques which result in random samples with a few different qualities.
Systematic sampling requires an approximated frame for a priori but not the full list. If the population order is random or random-like eg alphabetical then this method will give you a representative sample that can be used to draw conclusions about the population. It is a probability sampling method.
What is a Simple Random Sample.
ads
Citing Sources
Search This Blog
Labels
- 1000
- 1984
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- 2018
- ä¾å
- abbreviation
- abbreviations
- abide
- about
- abstract
- academic
- accept
- account
- accounting
- aces
- acknowledgement
- acknowledgements
- acknowledgment
- acronym
- action
- address
- adjective
- adjectives
- adviser
- affiliation
- after
- agreement
- agriculture
- aims
- alles
- alphabetical
- alphabetize
- alternative
- amazing
- amazon
- ambiguous
- american
- analyse
- analysis
- analyze
- annotated
- anonymous
- another
- answer
- apostrophe
- appendix
- application
- appointment
- approach
- approaches
- appropriate
- approximately
- architectural
- area
- argument
- argumentative
- around
- article
- articles
- aspirations
- assignment
- association
- assumption
- audience
- australia
- author
- authors
- auto
- automatic
- average
- avoid
- bachelor
- background
- ball
- bank
- banned
- based
- basics
- bear
- because
- before
- beginning
- being
- best
- between
- biased
- bible
- bibliographic
- bibliography
- bibme
- billion
- biography
- blind
- block
- blocking
- body
- book
- books
- break
- bullet
- business
- camera
- cannot
- capital
- capitalization
- capitalize
- capitalized
- cardinal
- career
- case
- catch
- catchy
- causal
- central
- change
- changes
- changing
- chapter
- characteristic
- charge
- chart
- check
- checker
- checkers
- checking
- chicago
- choose
- citation
- citations
- cite
- cited
- citer
- citing
- clarify
- class
- classification
- clauses
- coding
- collect
- collecting
- collection
- college
- collegiate
- colon
- colour
- comes
- comma
- commas
- common
- communication
- compare
- components
- compound
- concept
- conceptual
- concise
- conciseness
- conclusion
- conclusions
- confirm
- conjunction
- conjunctions
- construction
- contact
- containing
- content
- contents
- context
- continuous
- controlled
- convenience
- convert
- converter
- cool
- coordinating
- copied
- copy
- correct
- correction
- correlational
- correspondence
- corruption
- could
- countables
- cover
- create
- creating
- creator
- credible
- critical
- custodian
- data
- date
- dates
- deadline
- dedication
- deduction
- deductive
- default
- define
- defining
- definite
- definition
- degree
- dependent
- describe
- describing
- description
- descriptions
- descriptive
- design
- designs
- deutschland
- developer
- dialogue
- dictionary
- difference
- different
- direct
- disclosure
- discourse
- discuss
- discussion
- display
- dissertation
- distinguish
- docs
- doctor
- document
- documents
- docx
- does
- done
- down
- download
- draft
- easy
- easybib
- economic
- edit
- editing
- edition
- editor
- editors
- effective
- effectively
- elementary
- elements
- ellipses
- emotive
- empirical
- ending
- endnote
- endnotes
- engineering
- english
- equations
- equipment
- errors
- essay
- essays
- estilo
- evaluation
- evidence
- example
- examples
- experimental
- explain
- explained
- explanation
- expository
- express
- extended
- extension
- external
- face
- factor
- facts
- family
- fancy
- features
- figure
- figures
- file
- files
- findings
- first
- five
- fixer
- flexible
- focused
- follows
- font
- footnote
- footnotes
- form
- formal
- format
- formation
- formats
- formatting
- forms
- found
- four
- fraction
- framework
- france
- free
- freelance
- french
- from
- front
- full
- further
- future
- gather
- general
- generate
- generator
- geography
- german
- germany
- give
- glossary
- goals
- good
- government
- grade
- grammar
- grammarly
- great
- growth
- guide
- handbook
- happen
- harvard
- have
- having
- hdmi
- head
- header
- heading
- headings
- help
- helper
- history
- home
- hook
- however
- hundred
- hypothesis
- ideas
- identifying
- ieee
- illustration
- image
- images
- importance
- important
- improve
- included
- incorrect
- indefinite
- indent
- indentation
- independent
- index
- indirect
- induction
- inductive
- informal
- information
- initial
- inquisitive
- instead
- instructions
- inter
- interest
- interesting
- internal
- internet
- interview
- interviews
- into
- intranet
- introduce
- introducing
- introduction
- italicize
- italicized
- items
- itinerary
- jargon
- jobs
- join
- joint
- journal
- journals
- justification
- kindle
- kinds
- knowledge
- known
- label
- langer
- language
- large
- layout
- leadership
- lecture
- length
- letter
- letters
- level
- levels
- like
- limit
- limitations
- line
- lines
- linguistics
- link
- linking
- list
- lista
- literature
- logic
- login
- logistics
- long
- longer
- look
- looks
- lyrics
- machine
- magazine
- main
- make
- maker
- makes
- management
- manual
- manually
- manuscript
- many
- margins
- marketing
- marks
- mean
- meaning
- meanings
- meant
- measure
- measurement
- meeting
- mention
- merriam
- method
- methodology
- methods
- microsoft
- missing
- mistake
- model
- models
- modifier
- modifying
- more
- mosaic
- most
- movie
- movies
- much
- multiple
- music
- muss
- name
- names
- narrative
- naturalistic
- nature
- need
- netflix
- never
- newest
- news
- newspaper
- next
- night
- note
- noun
- nouns
- novel
- null
- number
- numbered
- numbers
- numerals
- objective
- objectives
- obvious
- office
- okay
- online
- openoffice
- order
- organise
- organization
- organized
- original
- other
- outline
- overall
- page
- pages
- paper
- papers
- paragraph
- paragraphs
- parallel
- paraphrase
- paraphrasing
- parenthesis
- parenthetical
- parenthetically
- part
- parts
- pass
- passive
- past
- paste
- patent
- patterns
- paypal
- people
- percentage
- perfect
- period
- person
- personal
- personality
- persuasive
- phrasal
- phrases
- physics
- pick
- picture
- pirate
- plagiarism
- plagiarized
- plan
- please
- plural
- poem
- poems
- poetry
- points
- polite
- political
- population
- possess
- possession
- possessive
- powerpoint
- poynter
- precis
- precise
- preliminary
- preposition
- prepositions
- present
- presentation
- press
- price
- primary
- printable
- private
- probability
- problem
- problems
- process
- professional
- professor
- program
- project
- projects
- pronoun
- pronouns
- proofread
- proofreading
- proper
- properly
- proposal
- psych
- psychological
- psychology
- publication
- published
- punctuation
- purdue
- purpose
- putting
- qualitative
- quality
- quantitative
- question
- questionnaire
- questions
- quick
- quiz
- quotation
- quote
- quotes
- quoting
- radio
- random
- rationale
- reading
- reasoning
- reasons
- redundancy
- reference
- references
- referencing
- refers
- region
- related
- relational
- relationship
- reliability
- remember
- remote
- report
- request
- require
- required
- research
- resources
- response
- results
- reuse
- review
- reviewing
- revision
- rhetorical
- right
- river
- rule
- rules
- runner
- safe
- sample
- sampling
- sayings
- scenes
- science
- scientific
- scope
- scratching
- search
- seasons
- second
- secondary
- section
- selection
- semicolon
- sentence
- sentences
- serbian
- series
- serve
- service
- services
- setup
- sheep
- sheet
- shona
- short
- shortcut
- shorten
- shortened
- should
- show
- sighted
- sign
- similar
- similarity
- simple
- singular
- site
- sites
- size
- slide
- small
- social
- software
- someone
- something
- songs
- source
- sources
- spaces
- spacing
- spanish
- speech
- spell
- spelling
- spss
- stable
- stage
- stages
- stanza
- start
- starters
- starting
- state
- statement
- statements
- stating
- statistics
- step
- steps
- story
- streaming
- structure
- structures
- student
- students
- study
- style
- styles
- subject
- subjective
- summarise
- summarize
- summarizing
- summary
- sure
- survey
- svenska
- synonym
- synopsis
- systematic
- table
- tables
- taboo
- take
- taken
- target
- teacher
- teachers
- techniques
- tekst
- tell
- template
- tense
- tenses
- tentative
- term
- terms
- test
- testing
- tests
- text
- textbook
- texting
- thanks
- that
- their
- thematic
- theme
- themes
- theoretical
- theory
- these
- thesis
- third
- those
- three
- through
- time
- times
- timetable
- title
- titles
- tone
- took
- tool
- tools
- topic
- topics
- track
- transcribe
- transcription
- transition
- transitional
- translated
- treatment
- trial
- turabian
- turn
- turnitin
- tweet
- types
- uber
- uncountable
- uncountables
- undergraduate
- union
- university
- unknown
- upload
- urkund
- usage
- used
- useful
- uses
- using
- vague
- valid
- validity
- vancouver
- variable
- variables
- various
- verb
- verbs
- versus
- very
- video
- visitor
- vocabulary
- voice
- voluntary
- water
- ways
- weak
- webpage
- website
- websites
- webster
- what
- whats
- when
- where
- whereas
- which
- widely
- wikipedia
- will
- with
- within
- without
- word
- words
- work
- works
- worth
- would
- write
- writing
- written
- york
- your
- yourself
- youtube
- youtuber
About Me
scratching on the 8 ball
Scratching On The 8 Ball Or 9 Ball Pool Rules LoveCueSports . Web Scratching on the 8 ball is considered a foul, as it is with 9 ball...

