Simply put qualitative analysis focuses on words descriptions or ideas while quantitative research focuses on numbers. In short its a collection of measurements or observations divided into two different types.
Programme information numbers involved what happens when who it is for cost participation levels.

Different types of qualitative data. For more details see our post qualitative vs quantitative data. Nominal data is also called the nominal scale. Or in the interpretation of images documents and videos.
Specifically the most popular and effective methods of qualitative data interpretation include the following. Here are the qualitative data collection methods. Focus groups A focus group is also among the most common types of qualitative research methods used.
The first type well talk about is what we call naturally occurring data. Here are examples of sources of quantitative and qualitative data. Qualitative models help individuals review and study various parts of information.
In-depth interview The in-depth interview is one of the most common types of qualitative research methods out there. Its usually descriptive and textual. Qualitative data refers to information about qualities or information that cannot be measured.
Nominal data and ordinal data. Binomial Data Nominal Data and Ordinal Data. Qualitative data is of two types namely.
Qualitative data consist of words pictures observations and symbols not numbers. When you classify or categorize something you create Qualitative or attribute data. Qualitative data explores the softer side of things.
This is done in a group discussion setting. The qualitative data can be broadly divided into Nominal Data and Ordinal Data. Ordinal data have a.
2 Types of Quantitative Data - Discrete Data and Continuous Data There are 2 types of quantitative data Discrete data and Continuous data. Examples include someones eye colour or the type of car they drive. Quantitative data is countable or measurable relating to numbers.
Lets summarize the key differences before exploring each aspect in more detail. The main differences between quantitative and qualitative data lie in what they tell us how they are collected and how they are analyzed. This week were looking at different types of qualitative data.
Different types of quantitative models include mathematical pictorial and analytic deduction. Qualitative data collection Qualitative data is information thats descriptive in nature. Qualitative data are also known as Categorical data.
Key Types of Qualitative Research Methods 1. Characteristics of Qualitative Data. Here a researcher uses different methods to gather data and understand the phenomenon.
It cannot be ordered and measured. Lastly this technique takes into account how participants feel about things during an event or activity. Documents archives maybe transcripts of speeches.
There are three main kinds of qualitative data. Qualitative data sometimes takes up numeric values but doesnt have numeric properties. Word and phrase repetitions scanning primary data for words and phrases most commonly used by respondents as well as words and phrases used with unusual emotions.
Generally QDA has 4 main steps. Statistics and statutory data. The qualitative data can be collected through deductive and inductive approaches by arranging organizing setting a code and validating the collected qualitative data and finally it is analyzed by set to give an appropriate solution to the problem.
Discrete data is information that can only take certain values and cant be made more precise. Qualitative data exists in the form of interviews focus groups or open-ended surveys. Qualitative data is descriptive relating to language.
Binary data place things in one of two mutually exclusive categories. Both primary and secondary data can be broken down into subcategories referred to as qualitative and quantitative data. These are data that exist without interaction from the researcher.
These methods include interviews visiting places observation surveys and reading documents. The group is limited to 6-10 people and a moderator is. But sometimes the data can be qualitative and quantitative.
It is one of the most commonly used data collection instruments for qualitative research. This is a common case in ordinal data. Logic is necessary to create a model that both captures the requisite information and produces expected results.
Getting feedback on a programme weekly check-ins surveys groups discussions before-and-after programme questions. Rightwrong truefalse or acceptreject. Nominal data is one of the types of qualitative information which helps to label the variables without providing the numerical value.
Then choose a simple random sample from each stratum. Systematic sample - A systematic sample is chosen on the basis of an ordered system.
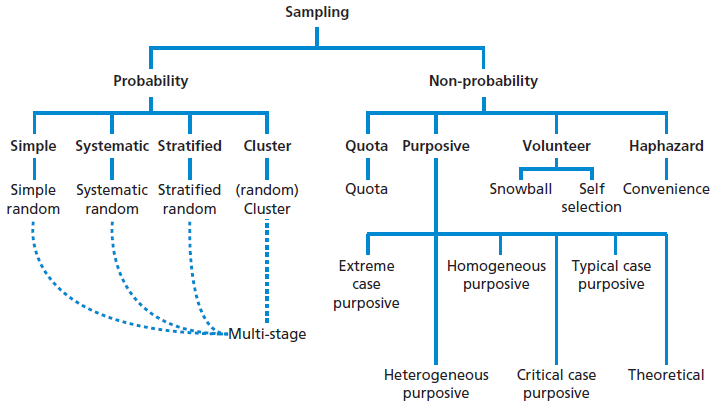
Multi-stage sampling is a combination of at least two methods of sampling.

What are the types of sampling. Sampling is a method used in statistical analysis in which a decided number of considerations are taken from a comprehensive population or a sample survey. To create a representative sample researchers take a simple random sample from each stratum. Combine those into the overall sample.
To Avoid Working Late A Quality Control Analyst Simply Inspects The First 100 Items Produced In A Day. Probability sampling Non-probability sampling. Probability samples or non-probability samples.
Types of Sampling We may then consider different types of probability samples. The selection of cases with maximum variation for the purpose of documenting unique or diverse variations that have emerged in adapting to different. Simple Random Stratified Systematic Or Convenience.
Cluster sample A cluster sample involves using a simple random sample of evident groups that the population contains. If the population is everyone who has bought a lottery ticket then each person has an equal chance of winning the lottery assuming they all have one ticket each. Although there are a number of different methods that might be used to create a sample they generally can be grouped into one of two categories.
Probability sampling where subjects are selected randomly or on a probability basis and the second is non-probability sampling where subjects. Divide the population into strata. Types of studies experimental vs.
Identify Which Of These Types Of Sampling Is Used. Techniques for random sampling and avoiding bias. O Convenience O Stratified O Systematic Simple Random.
Examples include the selection of extreme or deviant outlier cases for the purpose of learning from an unusual manifestations of phenomena of interest. There can be any number of these. Random sampling is a type of probability sampling where everyone in the entire target population has an equal chance of being selected.
This is the currently selected item. As suggested probability sampling is a type of sampling in which every single member of a group has an equal probability of being selected for the survey. Stratified sample - A stratified sample results when a population is split into at least two non-overlapping sub-populations.
This method can be used if the population has a. There are two types of sampling. There are two basic types of sampling methods.
Types of purposeful sampling designs There exist numerous purposeful sampling designs. Then a random sampling is done on those groups to get a sample. This is similar to the national lottery.
One study may incorporate several groups. Probability sampling can still exist within a filtered group such as American adults as long as every representative of this subgroup has an equal chance of. First the population is divided into non-overlapping subpopulations or groups.
Stratified sampling is a variation of random sampling that involves dividing the population into distinct groups or strata This method aims to make samples more representative of the population. The methodology used to sample from an extensive population depends on the type of study being conducted but may involve simple random sampling or systematic sampling. 9 rows Sampling in market research is of two types probability sampling and non-probability.
This is similar to the national lottery. There are a number of techniques of taking Probability sample.
Sampling Methods Types And Techniques Explained
Random sampling an.
5 types of sampling techniques. An example of this could be school or college. Now let us discuss three different types of sampling techniques in detail. There are two basic types of sampling methods.
TYPES OF SAMPLING 1. Before choosing a method the researcher must find a sampling frame this is the collection of people the researcher will then choose their sample from. All the members have an equal opportunity to be a part of the.
What is probability sampling. Units Types 516. The purest form of sampling under the probability approach random sampling provides equal chances of being picked for each member of the target population.
Types of Sampling Methods. Simple Random Sampling SRS Stratified Sampling Cluster Sampling Systematic Sampling. I Instantaneous sampling ii Natural sampling iii Flat top sampling Out of these three instantaneous sampling is called ideal sampling whereas natural sampling and flat-top sampling are called practical sampling methods.
Lets take a closer look at these two methods of sampling. The one chosen will depend on a number of factors such as time money etc. There are four types of Non-probability sampling techniques.
There are numerous ways of getting a sample but here are the most commonly used sampling methods. Supplies Glassware More 844 Understanding Laboratory Measurements. Every piece of research requires a sample and there are many ways of finding a suitable sample.
Sampling Techniques Basically there are three types of sampling techniques such as. The following sampling methods are examples of probability sampling methods. There are various sampling methods.
Probability sampling is a sampling technique where a researcher sets a selection of a few criteria and chooses members of a population randomly. Multiple or Double sampling. This is the currently selected item.
Non-probability sampling involves non-random selection based on convenience or other criteria allowing you to easily collect initial data. Types or Techniques Probability Sampling. There are four types of probability sampling techniques.
There are two types of sampling methods- 1 Random Sampling Method 2 Non-Random Sampling Method. But here only six important techniques have been discussed as follows. Sampling in market research is of two types probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
Includes Quota sampling Snowball sampling Judgment sampling a nd Convenience sampling furthermore Probability Sampling includes Simple random Stratified random Cluster sampling Systematic. In simple words probability sampling also known as random sampling or chance sampling utilizes random sampling techniques and principles to create a sample. Revise abiotic and biotic factors and sampling techniques such as using quadrats and pitfall traps as part of National 5 Biology.
Types of studies experimental vs. Sampling Techniques In Scientific Investigations 740 Chemistry Lab Equipment. Random sampling is a type of probability sampling where everyone in the entire target population has an equal chance of being selected.
Techniques for random sampling and avoiding bias.
In media communication research but also in the study of popular culture phenomena and which are use d to explore media content and its reception. Meaning Concept Utility Planning Organizing Conducting survey Public Opinion Survey Readership Survey.
Research Method Types In Social Sciences Google Search Research Methods Social Science New Product Development
Three types of research are described.

Types of research methods in media. Media as vehicles integrated media and method and media as learning context. Methods involving test subjects include surveys depth interviews focus groups and experiments. Quantitative research methods within Media Content Analysis point to a far more structured and consequently restricted form of gathering information from clips of media.
Media content analysis is a sub-set of content analysis and applies a systematic method to study mass media as texts including interview transcripts film narrative and forms TV. Fundamental or Pure Research. Types of Media Research.
These methods include content analysis surveys focus groups experiments and participant observation. Media research methods. Z receive a lecture on and discuss the purposes types and methods of research used in the media industries z visit library for introduction to cataloguing methods complex web searches use of journal searches etc.
In the field of communication there are three main research methodologies. Media research methods are the practical procedures for carrying out a research project. Definitions Methods Selection Formulation of Research Problem Hypothesis Sampling Research Designs Processing Analysis of data Statistical Analysis Findings Report Writing.
Next methodological disputes about the design of media studies that examine learning benefits are organized under two types of issues. Research methods are procedures for collecting and analyzing data. I used primary and secondary research methods in the research stages of my productsPrimary sources include - survey interview analyses of existing textsSecondary sources include internet research Wikipedia Google previous A-Level media studies blogs 3.
Types of research methods and research example Research methods are broadly classified as Qualitative and Quantitative. Research Methodologies for Media Research. Media research methods are the practical procedures for carrying out a research project.
Quantitative qualitative and rhetorical. Common methods include surveys experiments interviews and observations. The SAGE dictionary of social research methods.
As we have already discussed there are a lot of methods used in media or communication research. Media research is described from a social-psychological perspective. Explain what quantitative research can be used to find out in a Media context programme ratings readership circulation figures hits on a website box office figures sales of CDs and DVDs 3.
These methods include content analysis surveys focus groups experiments and participant observation. Is text should help you to de sign prepare. Research methods generally involve either test subjects or analysis of media.
Research methods generally involve either test subjects or analysis of media. Briefly describe some of the companies and organizations which provide the data -describe what info they provide and how they do it. Media Research- Types of Research.
Those related to studies media. Methods involving test subjects include surveys depth interviews focus groups and experiments. Thanks to advanced social listening and audience intelligence tools and platforms researchers today are able to aggregate data relating to specific events topics or within a specific.
The terms that define the scientific research method describe a procedure that has been accepted for centuries. As communication students progress in their careers they will likely find themselves using one of these far more often than the others. This type of research might involve types of field research such as interviews focus groups observation and others.
Social media research is the process of analyzing social media data to conduct quantitative and at times qualitative research in order to understand how audiences relate to topics by using tools and data extraction techniques. Scientific research is an organized objective controlled qualitative or quantitative empirical analysis of one or more variables. Research methods used in my media coursework.
Both methods have distinctive properties and data collection methods. Assignment 1 Research Methods and Techniques. The researchers aim to find out how the words and images are used and in what context.
This method includes interpreting words and images from a variety of documents music or other types of media. Media Research and Scientific Method. Qualitative methods involve a viewing of the clip and then unstructured open discussions.
These include Census Survey Observation Case Studies and interviews etc.
You can use the key variables like agricultural techniques type of soil environmental factors types of pesticides used the process of hybridisation type of yield obtained after hybridisation type of yield without hybridisation etc. Note that sometimes a variable can work as more than one type.
Variable Types And Examples Stats And R
There are three main types of variables in a scientific experiment.

Types of variables and examples. List five reasonable observed values. Variables are broadly categorised into. Nominal variables are variables that have two or more categories but which do not have an intrinsic order.
List five reasonable observed values. Types of variables in statistics - quantitative qualitative discrete continuous independent dependent. The word variable is derived from the root word vary meaning changing in amount volume number form nature or type.
An interval variable is similar to an ordinal variable except that the intervals between the values of the interval variable are equally spaced. Dependent variables which we. Dont use any of the examples already given in this handout.
Ask a good question about Types of Variables. An ordinal variable can also be used as a quantitative variable if the scale is numeric and doesnt need to be kept as discrete integers. On the other hand quantitative continuous variables are variables for which the values are not countable and have an infinite number of possibilities.
For simplicity we usually referred to years kilograms or pounds and centimeters or feet and inches for age weight and height respectively. In Java there are three types of variables. Scale - Strongly Disagree Disagree Neutral Agree Strongly Agree.
Rating - Very low Low Medium Great Very great. The next section provides examples of variables related to climate change academic performance crime fish kill and crop growth. The examples provided here are fairly basic.
Local Variables are a variable that are declared inside the body of a method. Give an example of a continuous quantitative random variable. For example a real estate agent could classify their types of property into distinct categories such as houses condos co-ops or bungalows.
Dont use any of the examples already given in this handout. An example of this type of variables can be the result of a sport competition first second or third place. Binary nominal and ordinal variables.
Learn about variables the different types of data that can be stored in a variable including ints floats objects structs and strings. Scientific research questions experiments and statistical data analysis can get very complex. Learning how to recognize the difference between independent and dependent variables will provide you with a strong foundation before you start learning about other types of variables.
There are three types of categorical variables. Independent variables which can be controlled or manipulated. Three variables one independent variable and two dependent variables.
Although they allude to attributes or qualities that lack a numerical value they are classified within a scale of value. Ordinary qualitative variables are known as semi-quantitative variables. These variables should be measurable ie they can be counted or subjected to a scale.
Categorical variables can be further categorized as either nominal ordinal or dichotomous. Lower the use of fertilizer improved seeds and modern equipments lower would be the agricultural productivity Four variable three independent variables and one dependent variable Higher the illiteracy in a society higher will be poverty and crime rate. Age sex export income and expenses family size country of birth capital expenditure class grades blood pressure readings preoperative anxiety levels eye color and vehicle type are all examples of variables because each of these properties varies or differs from one individual to another.
Instance variables are defined without the STATIC keyword They are defined Outside a method declaration.
ads
Citing Sources
Search This Blog
Labels
- 1000
- 1984
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- 2018
- ä¾å
- abbreviation
- abbreviations
- abide
- about
- abstract
- academic
- accept
- account
- accounting
- aces
- acknowledgement
- acknowledgements
- acknowledgment
- acronym
- action
- address
- adjective
- adjectives
- adviser
- affiliation
- after
- agreement
- agriculture
- aims
- alles
- alphabetical
- alphabetize
- alternative
- amazing
- amazon
- ambiguous
- american
- analyse
- analysis
- analyze
- annotated
- anonymous
- another
- answer
- apostrophe
- appendix
- application
- appointment
- approach
- approaches
- appropriate
- approximately
- architectural
- area
- argument
- argumentative
- around
- article
- articles
- aspirations
- assignment
- association
- assumption
- audience
- australia
- author
- authors
- auto
- automatic
- average
- avoid
- bachelor
- background
- ball
- bank
- banned
- based
- basics
- bear
- because
- before
- beginning
- being
- best
- between
- biased
- bible
- bibliographic
- bibliography
- bibme
- billion
- biography
- blind
- block
- blocking
- body
- book
- books
- break
- bullet
- business
- camera
- cannot
- capital
- capitalization
- capitalize
- capitalized
- cardinal
- career
- case
- catch
- catchy
- causal
- central
- change
- changes
- changing
- chapter
- characteristic
- charge
- chart
- check
- checker
- checkers
- checking
- chicago
- choose
- citation
- citations
- cite
- cited
- citer
- citing
- clarify
- class
- classification
- clauses
- coding
- collect
- collecting
- collection
- college
- collegiate
- colon
- colour
- comes
- comma
- commas
- common
- communication
- compare
- components
- compound
- concept
- conceptual
- concise
- conciseness
- conclusion
- conclusions
- confirm
- conjunction
- conjunctions
- construction
- contact
- containing
- content
- contents
- context
- continuous
- controlled
- convenience
- convert
- converter
- cool
- coordinating
- copied
- copy
- correct
- correction
- correlational
- correspondence
- corruption
- could
- countables
- cover
- create
- creating
- creator
- credible
- critical
- custodian
- data
- date
- dates
- deadline
- dedication
- deduction
- deductive
- default
- define
- defining
- definite
- definition
- degree
- dependent
- describe
- describing
- description
- descriptions
- descriptive
- design
- designs
- deutschland
- developer
- dialogue
- dictionary
- difference
- different
- direct
- disclosure
- discourse
- discuss
- discussion
- display
- dissertation
- distinguish
- docs
- doctor
- document
- documents
- docx
- does
- done
- down
- download
- draft
- easy
- easybib
- economic
- edit
- editing
- edition
- editor
- editors
- effective
- effectively
- elementary
- elements
- ellipses
- emotive
- empirical
- ending
- endnote
- endnotes
- engineering
- english
- equations
- equipment
- errors
- essay
- essays
- estilo
- evaluation
- evidence
- example
- examples
- experimental
- explain
- explained
- explanation
- expository
- express
- extended
- extension
- external
- face
- factor
- facts
- family
- fancy
- features
- figure
- figures
- file
- files
- findings
- first
- five
- fixer
- flexible
- focused
- follows
- font
- footnote
- footnotes
- form
- formal
- format
- formation
- formats
- formatting
- forms
- found
- four
- fraction
- framework
- france
- free
- freelance
- french
- from
- front
- full
- further
- future
- gather
- general
- generate
- generator
- geography
- german
- germany
- give
- glossary
- goals
- good
- government
- grade
- grammar
- grammarly
- great
- growth
- guide
- handbook
- happen
- harvard
- have
- having
- hdmi
- head
- header
- heading
- headings
- help
- helper
- history
- home
- hook
- however
- hundred
- hypothesis
- ideas
- identifying
- ieee
- illustration
- image
- images
- importance
- important
- improve
- included
- incorrect
- indefinite
- indent
- indentation
- independent
- index
- indirect
- induction
- inductive
- informal
- information
- initial
- inquisitive
- instead
- instructions
- inter
- interest
- interesting
- internal
- internet
- interview
- interviews
- into
- intranet
- introduce
- introducing
- introduction
- italicize
- italicized
- items
- itinerary
- jargon
- jobs
- join
- joint
- journal
- journals
- justification
- kindle
- kinds
- knowledge
- known
- label
- langer
- language
- large
- layout
- leadership
- lecture
- length
- letter
- letters
- level
- levels
- like
- limit
- limitations
- line
- lines
- linguistics
- link
- linking
- list
- lista
- literature
- logic
- login
- logistics
- long
- longer
- look
- looks
- lyrics
- machine
- magazine
- main
- make
- maker
- makes
- management
- manual
- manually
- manuscript
- many
- margins
- marketing
- marks
- mean
- meaning
- meanings
- meant
- measure
- measurement
- meeting
- mention
- merriam
- method
- methodology
- methods
- microsoft
- missing
- mistake
- model
- models
- modifier
- modifying
- more
- mosaic
- most
- movie
- movies
- much
- multiple
- music
- muss
- name
- names
- narrative
- naturalistic
- nature
- need
- netflix
- never
- newest
- news
- newspaper
- next
- night
- note
- noun
- nouns
- novel
- null
- number
- numbered
- numbers
- numerals
- objective
- objectives
- obvious
- office
- okay
- online
- openoffice
- order
- organise
- organization
- organized
- original
- other
- outline
- overall
- page
- pages
- paper
- papers
- paragraph
- paragraphs
- parallel
- paraphrase
- paraphrasing
- parenthesis
- parenthetical
- parenthetically
- part
- parts
- pass
- passive
- past
- paste
- patent
- patterns
- paypal
- people
- percentage
- perfect
- period
- person
- personal
- personality
- persuasive
- phrasal
- phrases
- physics
- pick
- picture
- pirate
- plagiarism
- plagiarized
- plan
- please
- plural
- poem
- poems
- poetry
- points
- polite
- political
- population
- possess
- possession
- possessive
- powerpoint
- poynter
- precis
- precise
- preliminary
- preposition
- prepositions
- present
- presentation
- press
- price
- primary
- printable
- private
- probability
- problem
- problems
- process
- professional
- professor
- program
- project
- projects
- pronoun
- pronouns
- proofread
- proofreading
- proper
- properly
- proposal
- psych
- psychological
- psychology
- publication
- published
- punctuation
- purdue
- purpose
- putting
- qualitative
- quality
- quantitative
- question
- questionnaire
- questions
- quick
- quiz
- quotation
- quote
- quotes
- quoting
- radio
- random
- rationale
- reading
- reasoning
- reasons
- redundancy
- reference
- references
- referencing
- refers
- region
- related
- relational
- relationship
- reliability
- remember
- remote
- report
- request
- require
- required
- research
- resources
- response
- results
- reuse
- review
- reviewing
- revision
- rhetorical
- right
- river
- rule
- rules
- runner
- safe
- sample
- sampling
- sayings
- scenes
- science
- scientific
- scope
- scratching
- search
- seasons
- second
- secondary
- section
- selection
- semicolon
- sentence
- sentences
- serbian
- series
- serve
- service
- services
- setup
- sheep
- sheet
- shona
- short
- shortcut
- shorten
- shortened
- should
- show
- sighted
- sign
- similar
- similarity
- simple
- singular
- site
- sites
- size
- slide
- small
- social
- software
- someone
- something
- songs
- source
- sources
- spaces
- spacing
- spanish
- speech
- spell
- spelling
- spss
- stable
- stage
- stages
- stanza
- start
- starters
- starting
- state
- statement
- statements
- stating
- statistics
- step
- steps
- story
- streaming
- structure
- structures
- student
- students
- study
- style
- styles
- subject
- subjective
- summarise
- summarize
- summarizing
- summary
- sure
- survey
- svenska
- synonym
- synopsis
- systematic
- table
- tables
- taboo
- take
- taken
- target
- teacher
- teachers
- techniques
- tekst
- tell
- template
- tense
- tenses
- tentative
- term
- terms
- test
- testing
- tests
- text
- textbook
- texting
- thanks
- that
- their
- thematic
- theme
- themes
- theoretical
- theory
- these
- thesis
- third
- those
- three
- through
- time
- times
- timetable
- title
- titles
- tone
- took
- tool
- tools
- topic
- topics
- track
- transcribe
- transcription
- transition
- transitional
- translated
- treatment
- trial
- turabian
- turn
- turnitin
- tweet
- types
- uber
- uncountable
- uncountables
- undergraduate
- union
- university
- unknown
- upload
- urkund
- usage
- used
- useful
- uses
- using
- vague
- valid
- validity
- vancouver
- variable
- variables
- various
- verb
- verbs
- versus
- very
- video
- visitor
- vocabulary
- voice
- voluntary
- water
- ways
- weak
- webpage
- website
- websites
- webster
- what
- whats
- when
- where
- whereas
- which
- widely
- wikipedia
- will
- with
- within
- without
- word
- words
- work
- works
- worth
- would
- write
- writing
- written
- york
- your
- yourself
- youtube
- youtuber
About Me
scratching on the 8 ball
Scratching On The 8 Ball Or 9 Ball Pool Rules LoveCueSports . Web Scratching on the 8 ball is considered a foul, as it is with 9 ball...

